TECHNOLOGIES
HPC computing
Microsoft Azure provides compute resources that make it possible to execute large HPC operations in the cloud. Microsoft Azure provides three types of HPC resources.
-
Big Compute with Azure Batch
-
Hybrid HPC in Azure with HPC Pack
-
Azure CycleCloud
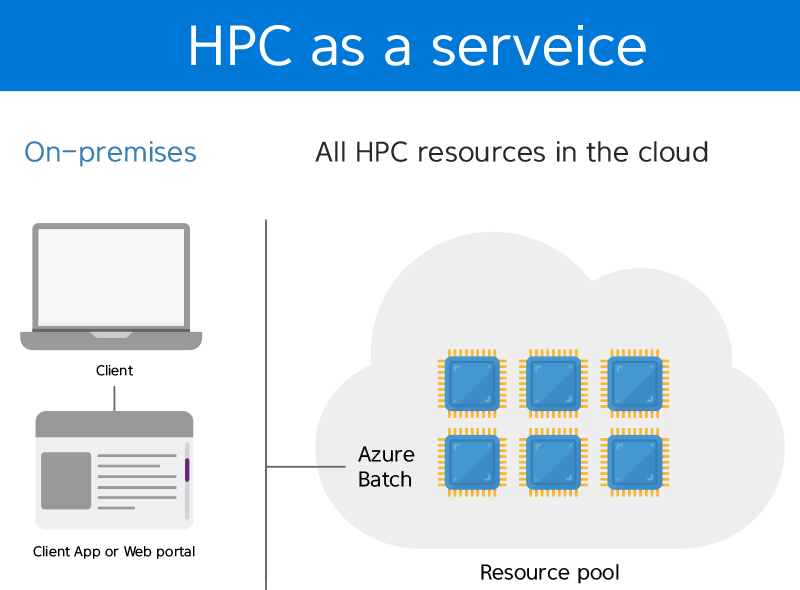
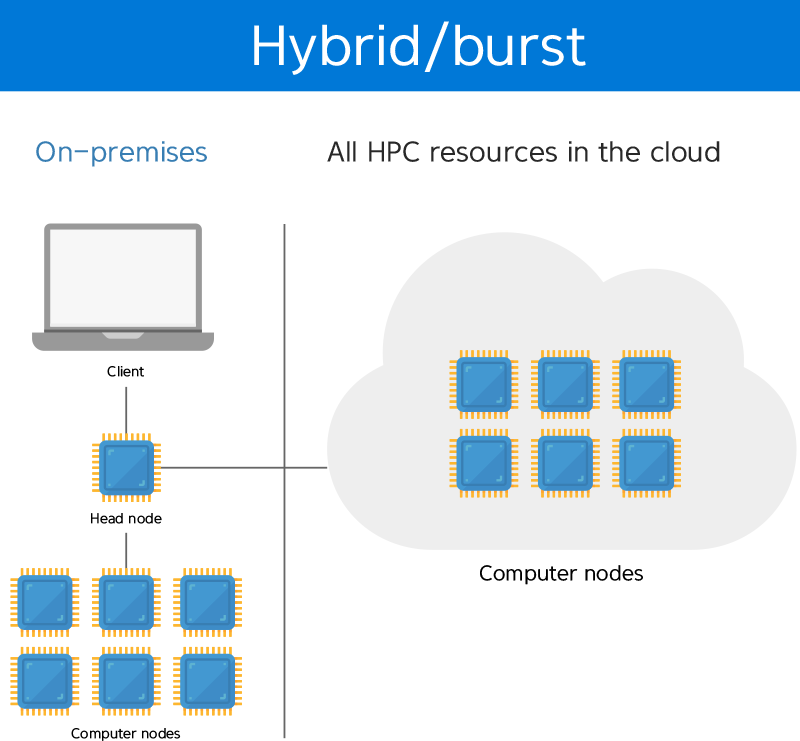
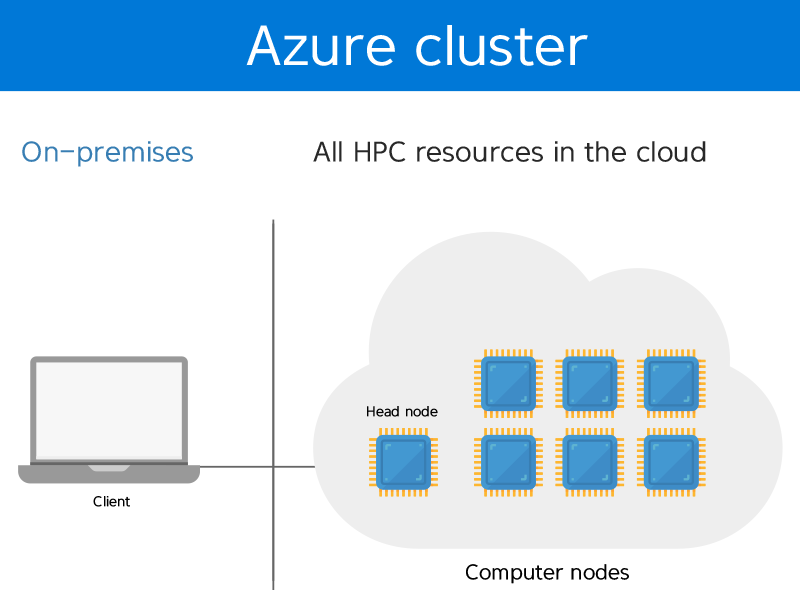
It is possible to utilize unlimited resources to do HPC (high-performance computing) jobs, e.g., large data analysis, simulation and financial modeling, experiments and reducing time to market.
Custom expansion and budget maintenance
If the quantity of data to collect and process increases, look at the cloud resources for flexibility in expanding the compute function. Azure’s HPC (high-performance computing) function enables cost-effective expansion.
Popularization of access to get results quickly
As data rapidly increases due to scientific experiments, the need to share, process and protect the data also increases. Joint expansion is possible anytime, anywhere, and safe access is provided to all users.
Time reduction
Providing more details and improved results by adding flexible computation resources After all, more projects can be completed, and more jobs can be performed.
Innovating the market with new products
No matter whether typical business app product groups are innovated, or proven scenarios are changed, or data-based overdrive is used, a quick and flexible architecture is required. Use Azure to build an architecture that can be expanded, adapted and reduced according to customer needs.
Azure can provide solutions optimized to help businesses address their challenges across different on-premise HPCs.
Technologies necessary for supporting HPC
- Virtual Machine: Close to unlimited computing power, including the GPU, Infiniband and the HPC Pack, which was used on-premise, will be configured the same way on the cloud.
- Virtual Network: Safe high-speed connection to on-premise through ExpressRoute
- Batch: Useful in compute-intensive asynchronous parallel execution
- CycleCloud: It comes with the tool for generating, managing, operating and optimizing Big Compute clusters.


